The Present continuous tense (also known as present progressive) is used to talk about actions that are happening right now, at the present moment. It can also be used to describe actions that are planned for the near future.
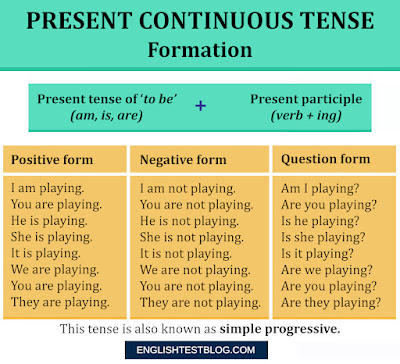
FormationThe present continuous tense is formed using a combination of three main elements.
- Subject (noun or pronoun): This is the person or thing performing the action.
- Present tense of to be (am, is, are): This verb changes depending on the subject.
- Present participle (verb + ing): This is the main action verb of the sentence. Add ing to the base form of the main verb to form the present participle.
Examples:
- I am playing.
- You are playing.
- He is playing.
- She is playing.
- It is playing.
- We are playing.
- You are playing.
- They are playing.
We form the negative of present continuous by simply adding the word not after the verb to be.
Negative form: Subject + to be + not + present participle.
Examples:
- I am not playing.
- You are not playing.
- He is not playing.
- She is not playing.
- It is not playing.
- We are not playing.
- You are not playing.
- They are not playing.
We form question sentences in this tense by reversing the verb to be and the subject.
Question form: To be + subject + present participle?
Examples:
- Am I playing?
- Are you playing?
- Is he playing?
- Is she playing?
- Is it playing?
- Are we playing?
- Are you playing?
- Are they playing?
We can also use the present continuous with the question words who, what, where, when, why, and how.
Examples:
- What are you doing?
- Where is she going?
- Who is talking?
Uses
We use the present continuous to talk about:
1. actions happening at the time of speaking.
Examples:
- Where's John? He is playing basketball in the park.
- Why are you sitting at my desk? Are you looking for something?
- Sorry, I'm busy at the moment. I'm writing an essay.
2. actions happening around now, but not at the exact time of speaking.
Examples:
- He is teaching German and learning French.
- They are building their own house near the beach.
- They are staying in the same hotel.
3. future plans and arrangements, especially when they are already confirmed or decided.
Examples:
- We are having a party on Saturday.
- He is starting his new job next month.
- They are traveling to Italy in June.
4. changing situations, especially with these verbs: become, get, grow, change, increase, rise, or fall.
Examples:
- My English is getting better.
- The children are growing up quickly.
- The company is improving its service.
Verbs NOT usually used in Present Continuous
We cannot use stative verbs with the present continuous (or any other continuous tenses). For stative verbs, use present simple.
Examples:
- I understand you. (NOT I
am understandingyou.) - This soup tastes delicious. (NOT This soup
is tastingdelicious.) - Do you want some tea? (NOT
Areyouwantingsome tea?)
Time expressions
We can use the present continuous with now, right now, at the moment, today, this week, this month, and this year.
Examples:
- She is studying for her exam now.
- We are cleaning the house at the moment.
- They are visiting the museum today.
The difference from the Present Simple
The present continuous tense is different from the present simple tense, both in structure and use. The present continuous describes actions happening right now or around the present moment. The present simple typically describes facts, general truths, routines, habits, or permanent situations.
Examples:
- Present simple: She speaks English fluently.
- Present continuous: She is speaking with the manager now.

Comments
Post a Comment